Liver fibrosis is a silent yet serious condition that often progresses without obvious symptoms in its early stages. Many patients in Pune and Pimpri-Chinchwad (PCMC) are diagnosed only after the disease has already advanced. Raising awareness about the early warning signs of liver fibrosis and the availability of advanced diagnostic tests is essential to prevent permanent liver damage.
What Is Liver Fibrosis?
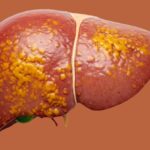
Liver fibrosis refers to the formation of scar tissue in the liver as a response to repeated or long-term liver injury. When healthy liver tissue is damaged repeatedly, it is replaced by fibrous scar tissue. Over time, this scarring can interfere with normal liver function and may progress to cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer if left untreated.
Fibrosis itself is not a disease but a reaction to chronic liver injury, commonly caused by:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Chronic hepatitis B or C infection
- Alcohol-related liver disease
- Autoimmune liver disorders
- Metabolic and genetic liver conditions
- Long-term exposure to certain medications or toxins
The good news is that liver fibrosis can be slowed, halted, or even reversed if detected early and managed appropriately by a specialist.
Early Symptoms of Liver Fibrosis
One of the biggest challenges with liver fibrosis is that it is often asymptomatic in the early stages. Many patients feel completely normal, allowing the condition to go undetected for years.
However, some subtle early symptoms may include:
- Persistent fatigue or low energy levels
- Mild discomfort or heaviness on the right side of the upper abdomen
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight changes
- Abdominal bloating or digestive discomfort
These symptoms are often mistaken for lifestyle-related issues or stress, which is why liver fibrosis is frequently overlooked.
As fibrosis progresses, more noticeable symptoms may appear, such as:
- Swelling of the legs or abdomen
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- General weakness and reduced stamina
At this stage, prompt medical evaluation becomes critical.
Causes and Risk Factors of Liver Fibrosis
Liver fibrosis usually develops due to chronic, ongoing liver damage. One of the most common causes today is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which is closely linked to modern lifestyle factors.
Key risk factors include:
- Obesity and central fat accumulation
- Type 2 diabetes
- High cholesterol and triglyceride levels
- Metabolic syndrome
- Chronic alcohol consumption
- Viral hepatitis (B or C)
- Autoimmune liver diseases
- Family history of liver disease
Individuals with a sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet, or existing metabolic conditions should undergo regular liver health evaluation.
Diagnosis of Liver Fibrosis Using Advanced Testing
Early diagnosis plays a crucial role in preventing disease progression. Today, state-of-the-art, non-invasive tests allow accurate detection of liver fibrosis without the need for surgery.
Common diagnostic tools include:
- Blood tests: Liver function tests and fibrosis markers
- Ultrasound abdomen: Initial screening tool
- FibroScan: Measures liver stiffness and fibrosis severity
- CT scan or MRI: Used in selected cases for detailed imaging
A liver biopsy is rarely required and is reserved for unclear or advanced cases. Consulting an experienced gastroenterologist or hepatologist ensures correct staging and avoids misdiagnosis.
Importance of Early Specialist Consultation
Liver fibrosis reflects not just liver health but overall metabolic well-being. Early consultation with a specialist allows:
- Accurate diagnosis and staging
- Identification of underlying causes
- Timely lifestyle and medical intervention
- Prevention of progression to cirrhosis
People with diabetes, obesity, abnormal liver tests, or a family history of liver disease should seek medical advice promptly. Avoid self-medication or unverified remedies, as they may worsen liver damage.
Conclusion
Liver fibrosis often develops silently, but its consequences can be severe if ignored. Recognizing early symptoms and undergoing timely evaluation using modern diagnostic tools can make a significant difference. With early detection and expert care, liver fibrosis can often be controlled or reversed, protecting long-term liver function.
If you are at risk or experiencing persistent fatigue, abdominal discomfort, or abnormal liver reports, consult a qualified gastroenterologist for a comprehensive liver assessment.